The Transformative Power of 3D Prototyping in Metal Fabrication
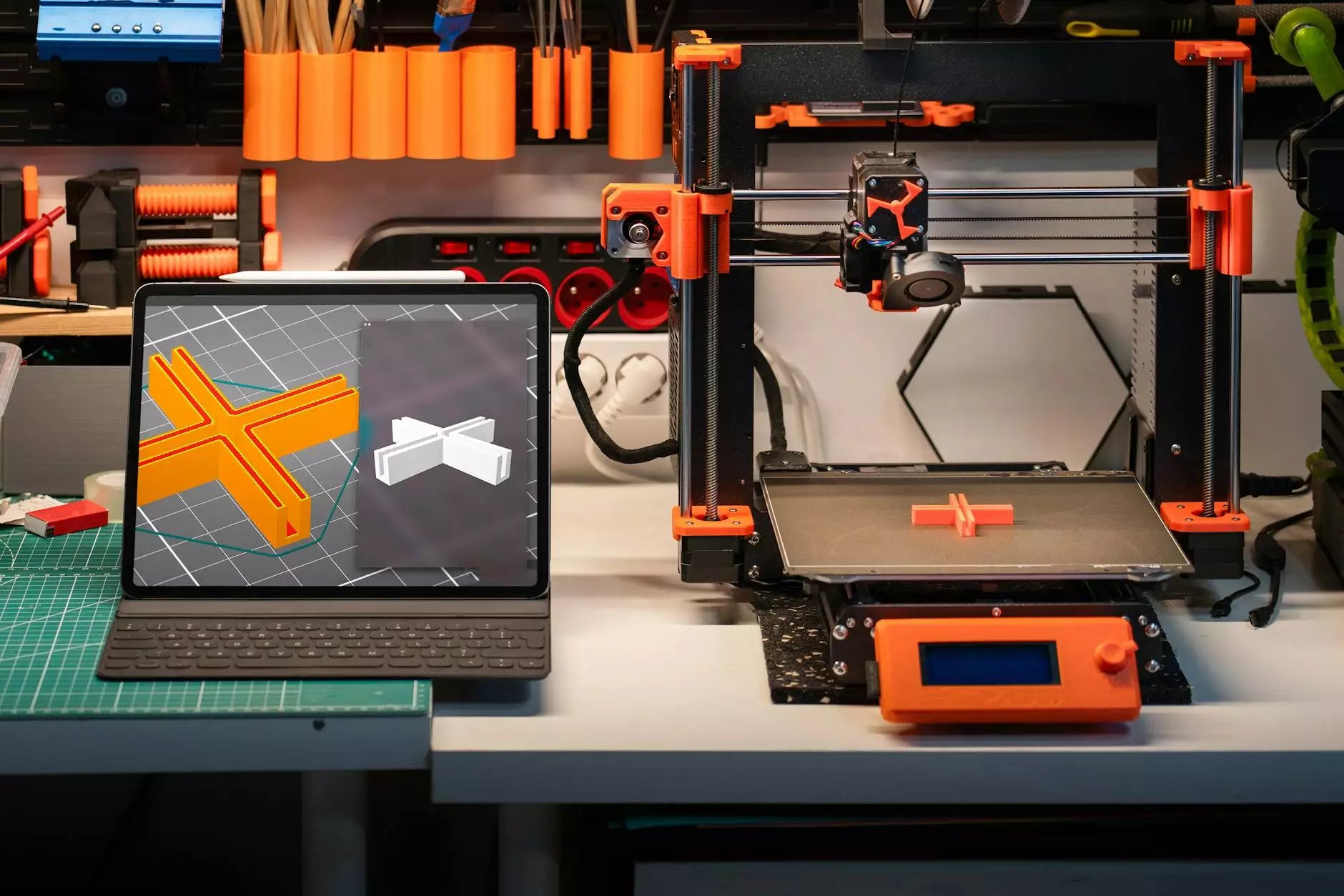

Introduction to 3D Prototyping
In the evolving landscape of manufacturing, 3D prototyping has emerged as a groundbreaking technique that is reshaping the processes of design, creation, and production. This advanced technology allows designers and engineers to produce accurate prototypes quickly, facilitating an efficient transition from concept to final product.
What is 3D Prototyping?
3D prototyping involves using various additive manufacturing technologies to create three-dimensional objects from digital files. Unlike traditional subtractive methods that carve away material, 3D printing builds components layer by layer, which offers substantial advantages in terms of material usage and design complexity.
Benefits of 3D Prototyping in Metal Fabrication
The integration of 3D prototyping into metal fabrication presents numerous benefits that drive innovation and efficiency. Here are some of the most significant advantages:
- Reduced Time to Market: Rapid prototyping accelerates the development process, enabling companies to bring products to market much faster.
- Cost-Effective Production: Decreases in waste and efficiency in material usage lower production costs significantly.
- Design Flexibility: Allows for complex geometries and shapes that are often impossible with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Enhanced Testing and Iteration: Quick turnaround for prototypes means that designs can be tested and refined effectively before mass production.
- Customization: Products can be tailored to specific needs or preferences with relative ease.
The Process of 3D Prototyping
Understanding the 3D prototyping process is essential for any business looking to adopt this technology. The typical workflow includes:
- Design: The product is designed using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to create a detailed 3D model.
- Slicing: The 3D model is sliced into layers by specialized software, converting the design into a format that 3D printers can interpret.
- Printing: The slicing software sends instructions to the 3D printer, which constructs the prototype layer by layer using metal filaments or powders.
- Post-Processing: Once printed, the prototype may require additional steps like polishing, heat treatment, or surface finishing.
- Testing and Feedback: The prototype is subjected to rigorous testing to ensure it meets all specifications and performance criteria.
Innovative Applications of 3D Prototyping in the Metal Fabrication Industry
The versatility of 3D prototyping has led to exciting applications across various sectors, particularly in metal fabrication. Here are a few notable examples:
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace sector has been one of the earliest adopters of 3D prototyping, utilizing it to produce lightweight components that enhance fuel efficiency and performance. Complex parts can be fabricated that significantly reduce weight while maintaining structural integrity.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, 3D prototyping allows manufacturers to test innovative designs and improve fuel economy. Companies can rapidly prototype parts that are tailor-made for specific models or consumer preferences.
Medical Devices
The medical field benefits from 3D prototyping by creating customized implants and prosthetics. This technology enables surgeons to plan procedures more effectively and to produce devices that are specifically designed for individual patients’ anatomy.
Challenges and Considerations
While 3D prototyping offers numerous benefits, it is not without challenges. Companies must consider the following factors:
- Material Limitations: Not all metals are suitable for 3D printing, and the choice of material can significantly impact the properties of the final product.
- Initial Investment: The cost of high-quality 3D printers and materials can be substantial, particularly for small businesses.
- Technical Skill Requirement: Companies need staff with the technical knowledge to operate and maintain 3D printers and to design prototypes efficiently.
Future of 3D Prototyping in Metal Fabrication
The future of 3D prototyping looks promising, with advancements in technology continuously expanding its capabilities. Innovations in materials, such as new metal alloys and composites, will further enhance the properties of prototypes. Additionally, as software for design and simulation becomes more sophisticated, the efficiency and accuracy of 3D prototyping will continue to improve, allowing for even more complex and optimized designs.
Conclusion
As the metal fabrication industry continues to evolve, 3D prototyping stands at the forefront of this transformation. By embracing this innovative technology, businesses not only enhance their productivity and creativity but also position themselves to thrive in a competitive landscape. The potential of 3D prototyping is vast, and its impact on the future of manufacturing cannot be overstated.
For businesses in the metal fabrication sector, exploring the integration of 3D prototyping through expert partners, like those at DeepMould, can pave the way for unprecedented growth and innovation.